Definition[]
Modulation is
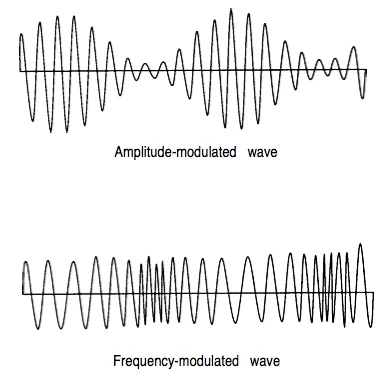
| “ | the process of encoding information onto a radio wave by varying one of its basic characteristics — amplitude, frequency, or phase — in relation to an input signal such as speech, music, or video. The input signal, which contains the information to be transmitted, is called the modulating or baseband signal. The radio wave that carries the information is called the carrier wave. The radio wave that results from the combination of these two waves is called a modulated carrier. Two of the most common types of modulation are amplitude modulation (AM) and frequency modulation (FM).[1] | ” |