Definition[]
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is
| “ | a standard network protocol used to transfer computer files from one host to another host over a TCP-based network, such as the Internet.[1] | ” |
Overview[]
The protocol allows a user to log onto a remote computer, and retrieve text, graphics, audio, or computer program files, and transfer the desired files back to its computer. The FTP allows computers connected to the Internet to exchange files, regardless of the computer platform.
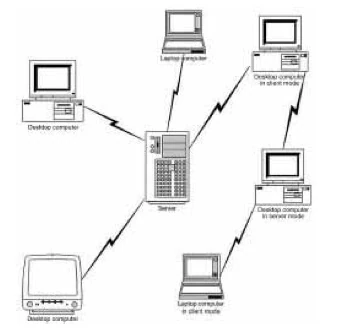
How it works[]
FTP is based on a client-server model. Any computer can act as either a client or a server. "FTP users may authenticate themselves using a clear-text sign-in protocol but can connect anonymously if the server is configured to allow it."[2]
Some common FTP client programs include Web browsers, WS-FTP (Light Edition & Pro), War FTP Daemon, CuteFTP, BulletProof FTP, and FTP Voyager. The client-server model is similar to a central file cabinet in an office where people can access documents.
FTP uses two ports — data is transferred on port 20, while control information is exchanged on port 21.
References[]
- ↑ ARSC Guide to Audio Preservation, Glossary, App. B, at 226.
- ↑ Inventory of Standards Relevant to Cloud Computing.